The world of cannabinoids is diverse and fascinating. More and more people are interested in the differences between CBD (cannabidiol) , CBG (cannabigerol) , and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) . Although all three substances originate from the cannabis plant, they have very different effects on the body and mind. This article explains the most important differences and gives you a clear overview.
1. What is CBD?
CBD (Cannabidiol) is one of the best-known cannabinoids. It is not psychoactive, meaning it does not cause a "high". CBD is often valued for its relaxing and balancing properties . Studies show that it can be helpful for, among other things:
Stress and unrest
Sleep problems
Inflammation and pain
Products with CBD, such as oils, capsules or cosmetics, are very popular because they are legally available and have no intoxicating effect.
2. What is CBG?
CBG (Cannabigerol) is often referred to as the "mother of all cannabinoids" because many other cannabinoids – including CBD and THC – are derived from CBG. Although CBG is even less researched than CBD, current studies show interesting potential:
Supporting concentration
Promoting inner balance.
Possible antibacterial effect
CBG is found in many full-spectrum extracts, but is also increasingly offered as pure CBG oil .
3. What is THC?
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the psychoactive component of the cannabis plant. It is primarily responsible for the "high" feeling . In addition to its intoxicating effect, THC also has medical potential, for example in the following cases:
Chronic pain
Lack of appetite
Nausea (e.g. due to chemotherapy)
In Germany, THC is only legally available with a doctor's prescription.
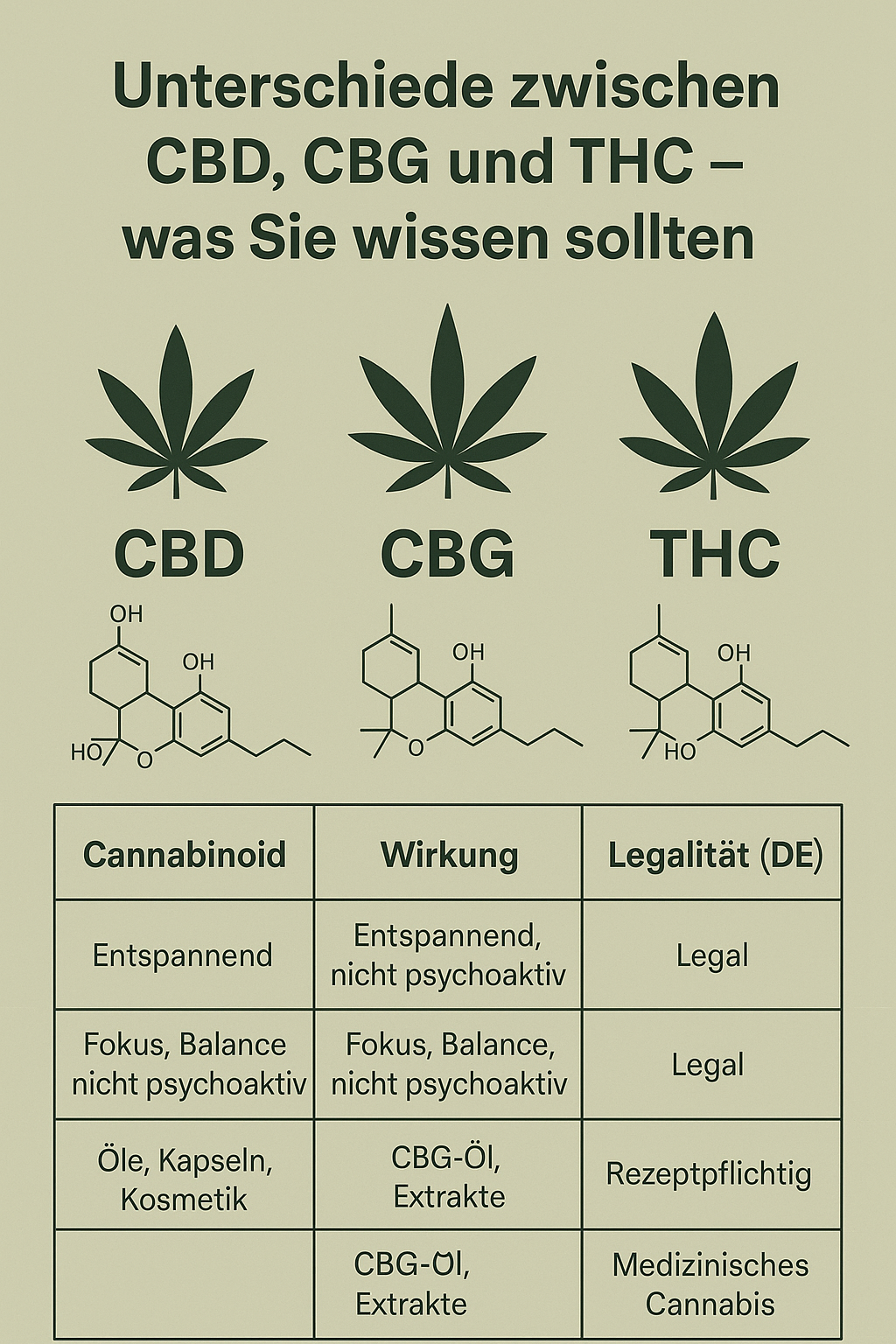
4. The most important differences at a glance
Cannabinoid
Effect
Legality (DE)
Typical products
CBD
Relaxing, not psychoactive
Legal
Oils, capsules, cosmetics
CBG
Focus, balance, not psychoactive
Legal
CBG oil, extracts
THC
Psychoactive, intoxicating
Prescription required.
Medical Cannabis
5. Conclusion
While CBD and CBG have many positive properties and are legally available, THC is strictly regulated due to its psychoactive effects. Anyone wishing to use cannabinoids should inform themselves thoroughly and pay attention to high-quality products .
Whether for more relaxation, concentration or well-being - knowing the differences between CBD, CBG and THC is the key to making a conscious decision.